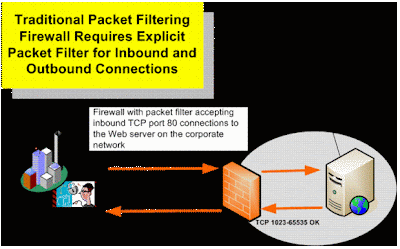
The general reasoning behind firewall usage is that without
a firewall, a subnet's systems expose themselves
to inherently insecure services such as NFS or NIS and to probes and attacks
from hosts elsewhere on the network. In a firewall-less environment, network
security relies totally on host security and all hosts must, in
a sense, cooperate to achieve a uniformly high level of
security. The larger the subnet, the less manageable it is to maintain all
hosts at the same level of security. As mistakes and lapses in security become
more common, break-ins occur not as the result of complex attacks, but because
of simple errors in configuration and inadequate passwords.
A firewall approach
provides numerous advantages to sites by helping to increase overall host
security. The following sections summarize the primary benefits of using a
firewall.
·
A
firewall can greatly improve network security and reduce risks to hosts on the
subnet by filtering inherently insecure services. As a result, the subnet
network environment is exposed to fewer risks, since only selected protocols
will be able to pass through the firewall.
·
For
example, a firewall could prohibit certain vulnerable services such as NFS from
entering or leaving a protected subnet. This provides the benefit of preventing
the services from being exploited by outside attackers, but at the same time
permits the use of these services with greatly reduced risk to exploitation.
Services such as NIS or NFS that are particularly useful on a local area
network basis can thus be enjoyed and used to reduce the host management
burden.
·
Firewalls
can also provide protection from routing-based attacks, such as source routing
and attempts to redirect routing paths to compromised sites via ICMP redirects.
A firewall could reject all source-routed packets and ICMP redirects and then
inform administrators of the incidents
·
A
firewall also provides the ability to control access to site systems. For
example, some hosts can be made reachable from outside networks, whereas others
can be effectively sealed off from unwanted access. A site could prevent
outside access to its hosts except for special cases such as mail servers or
information servers. This brings to the fore an access policy that firewalls
are particularly adept at enforcing: do not provide access to hosts or services
that do not require access. Put differently, why provide access to hosts.
·
services
that could be exploited by attackers when the access is not used or required?
If, for example, a user requires little or no network access to her desktop
workstation, then a firewall can enforce this policy.
·
A
firewall can actually be less expensive for an organization in that all or most
modified software and additional security software could be located on the
firewall systems as opposed to being distributed on many hosts. In particular, one-time
password systems and other add-on authentication software could be located at
the firewall as opposed to each system that needed to be accessed from the
Internet.
·
Other
solutions to network security such as Kerberos [NIST94c] involve modifications at each host
system. While Kerberos and other techniques should be considered for their
advantages and may be more appropriate than firewalls in certain situations,
firewalls tend to be simpler to implement in that only the firewall need run
specialized software.
·
Privacy
is of great concern to certain sites, since what would normally be considered
innocuous information might actually contain clues that would be useful to an
attacker. Using a firewall, some sites wish to block services such as finger and Domain Name Service. finger displays information about
users such as their last login time, whether they've read mail, and other
items. But, finger could leak
information to attackers about how often a system is used, whether the system
has active users connected, and whether the system could be attacked without
drawing attention.
·
Firewalls
can also be used to block DNS information about site systems, thus the names
and IP addresses of site systems would not be available to Internet hosts. Some
sites feel that by blocking this information, they are hiding information that
would otherwise be useful to attackers.
·
If
all access to and from the Internet passes through a firewall, the firewall can
log accesses and provide valuable statistics about network usage. A firewall,
with appropriate alarms that
sound when suspicious activity occurs can also provide details on whether the
firewall and network are being probed or attacked.
·
It is important to collect network usage
statistics and evidence of probing for a number of reasons. Of primary
importance is knowing whether the firewall is withstanding probes and attacks,
and determining whether the controls on the firewall are adequate. Network
usage statistics are also important as input into network requirements studies
and risk analysis activities.
·
Lastly, but perhaps most importantly,
a firewall provides the means for implementing and enforcing a network access
policy. In effect, a firewall provides access control to users and services.
Thus, a network access policy can be enforced by a firewall, whereas without a
firewall, such a policy depends entirely on the cooperation of users. A site
may be able to depend on its own users for their cooperation, however it cannot
nor should not depend on Internet users in general.